Anyone who has ever traded forex would know the importance of the Federal Reserve Bank’s monetary policy meeting. Commonly referred to as the Fed, the Fed meeting is one of those few fundamental events that can move the markets.
If you are new to the trading scene or do not have much grasp on the economics, this article will walk you through the Fed funds rate. By the end of this article, you will learn what the Fed funds rate is all about and why it matters so much for traders.
You will also be able to learn about why the Fed funds rate is so important and why you as a trader should pay attention to this.
What is the Fed funds rate?
The Fed funds rate, as the name suggests is the interest rate that the Federal Reserve Bank controls. In doing so, it can influence the interest rates across all the different markets and horizons.
The Fed funds rate has an impact to influence the interest rates in everyday life, ranging from mortgage rates to personal or car loans in the U.S., as well as impacting global forex markets as well. Since the Federal Reserve is the central bank for the world’s reserve currency, it shouldn’t be surprising why these rates are so important for the markets.
Traders across the spectrum, from fixed income to equities and forex and even commodities pay attention to the Fed funds rate.
The Fed funds rate is simply the interest rate that the Fed charges for banks that have their deposits held at the central bank. Typically, the Fed sets a lower and upper range of the fed funds rate. The Fed funds rate or the effective fed funds rate is the median rate between these two thresholds.
Fed funds rate explained
The fed funds rate is not as simple as the Fed mentioning a few numbers depicting the threshold. On the contrary, the Fed funds rates are set up via something called the open market operations. The open market operations are done via buying and selling of government securities with the various investment and commercial banks.
When the Fed wants to hike the Fed funds rate, it does so by selling the government securities to these banks. The government securities are nothing much the U.S. Treasury-issued instruments, namely short-term bills, that mature in under 12 months.
On the contrary, when the Fed wants to cut interest rates, it does so by selling these government securities.
In both instances, the main common denominator is for the Federal Reserve Bank to increase or decrease the money supply. Since the Fed funds rates form the core of the Fed operations, this increase or decrease in money supply can impact the borrowing costs.
Simply put, when a commercial bank wants to raise additional funds, one of the ways is to buy or sell its government treasury instruments. Depending on how the Fed’s cycle is, this interest rate, with the fixed income instruments as collateral can see higher or lower borrowing costs.
The commercial bank in turn passes this cost on to its customers. However, the pass-through of the Fed funds rate is not straightforward. In many cases, the commercial bank can also add its own spread on top of the Fed funds rate.
This spread merely reflects other aspects such as counterparty credit risk among other things.
What is the Effective Fed Funds Rate?
The correct terminology for the Fed funds rate is known as the effective fed funds rate. It reflects the interest charged on unsecured borrowing by depository institutions. Also known as the EFFR for short, it is the volume-weighted median of the overnight fed funds transaction.
The EFFR or the Fed funds rate is published for the prior business day. This means that there is a one-day lag for the EFFR as it is based on closed transactions.
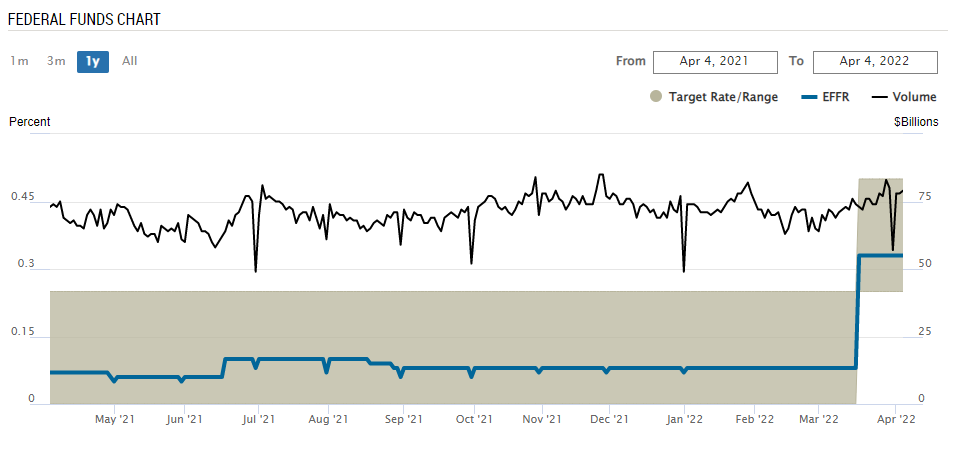
The above chart shows a comparison of the Fed target rate or range and the actual or the effective fed funds rate. On the right-hand side of the scale, depicted by the black line is the daily volume of transactions.
The shaded boundaries form the upper and lower end of the range for the Fed funds rate. The thicker blue line indicates the effective fed funds rate. You can notice how the EFFR stays well within the range specified by the Fed.
After learning about how the Fed funds rate is set, the obvious question that comes to mind is why the Fed raise (or cut) rates.
Why does the Fed raise or cut interest rates?
Interest rates are a monetary policy mechanism used by central banks across the world. Through this tool, central banks can control the speed of the economy.
When the economy is overheating, as seen when inflation starts to rise rapidly combined with the economic growth peaking, the central bank can be set up. This is controlled by removing excess money supply from the market.
As we learned earlier, the Fed uses open market operations in order to increase or reduce the money supply in the market. The reverse repo transactions are used by the central bank, such as the Fed to raise the money supply.
The reverse repo is a term where the central bank agrees to purchase securities from depository institutions, with the pledge to sell them back to the original counterparty, albeit at a slightly higher price.
Readers should note that the repo rate is not the same as the EFFR. In fact, the repo rate includes the EFFR as well as the transactions based on the Eurodollar market activity as well.
The repo rate in the U.S. is referred to as the overnight bank funding rate or OBFR. The next chart below shows the relationship between the OBFR and the EFFR. The OBFR rate is always lower than the EFFR.
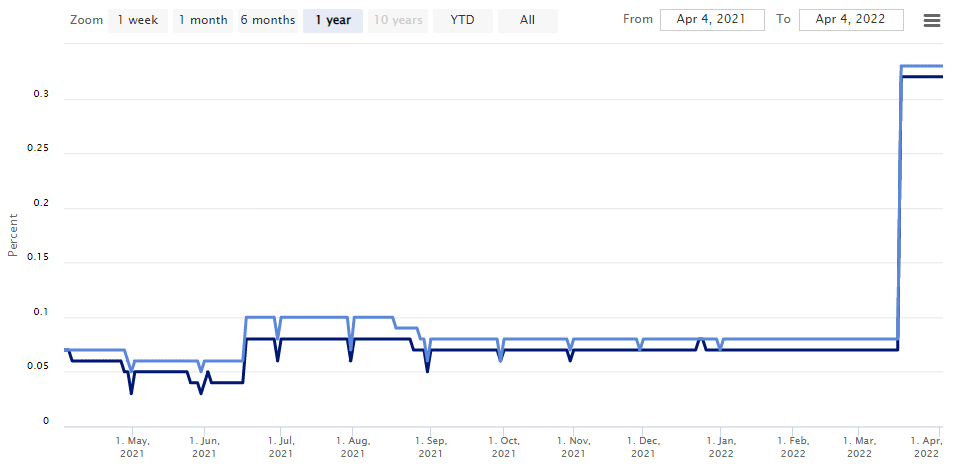
In terms of trading volumes, the EFFR has a slightly lower transaction volume level compared to the OBFR. The reason behind this is because transactions in EFFR are mainly limited to the depository institutions whereas the OBFR boasts of the broader Eurodollar market, used by a wider market.
Thus, by raising and cutting interest rates, the Federal Reserve basically acts as a driver of a car, accelerating or decelerating in order to keep economic growth at a steady rate.
Fed funds rate history - Fed funds rate chart
In the recent decade, the Fed funds rate has been broadly stale. Since the 2008 global financial crisis, the rate has been sitting near the zero level.
While interest rates rose slightly after the economy picked up a few years later, the recent Covid-led disruptions saw the Fed cut rates back to near zero. Prior to the GFC era, interest rates were quite higher.
The chart below shows the Fed funds rate since 1955.

Although the interest rate has been moving on a downward trajectory, interest rates hit an all-time high of close to 20% in the 1980’s. It was in this period that the Fed was engaged in fighting inflation. U.S. consumer prices rose to the highest level of 14.6%
It is not surprising then that the recent rise in consumer prices has evoked memories of this period. Still, interest rates are currently near zero and hence, the increase may not be as high as it once was. However, it still warrants interest from the markets at large in how the Fed will continue to fight inflation in the current times.
What happens to the dollar when interest rates rise?
Given that we now have an understanding of the Fed funds rate, how it is set and the reasons behind it, let’s look at how its impact is felt on the U.S. dollar. If you have watched the U.S. dollar during any of the Fed meetings, it won’t be a surprise.
The USD is very sensitive to interest rate changes. It is not just changing, but as well as what is known as Fed-speak.
Fed speak is the terminology given, when various members of the FOMC talk and give their views on the economy and thus where interest rates should be. Since the Fed interest rates are based on a voting system, the comments from individual voting members matter.
In the forex markets, the relationship between the Fed funds rate and the U.S. dollar is not straightforward. Meaning that the US dollar will not rise as a direct result of the higher fed funds rate, and likewise, the USD will not fall as a direct result of lower interest rates.
Initially, as a knee-jerk reaction one may see the USD appreciate in response to positive rate adjustments. Likewise, the dollar also tends to fall initially during a rate cut. All said and done, there are a lot more things to look into.
The Fed does not cut or raise rates out of the blue
Firstly, the Federal Reserve does not simply raise rates out of the blue. There are a few exceptions such as the Fed’s response to the Covid-19 pandemic. But these were times of panic and the markets were looking for cues from the Fed.
Such moments are exceptional and far and few between. Using such a strategy is usually derived on the back of creating a shock and awe. This shock and awe can be in order to stem the dollar’s strength or to create a strong impression in the market.
The Fed usually communicates rate changes beforehand
Under normal circumstances, the Fed follows a well-laid-out plan. This means that prior to the rate hike or rate cut, members of the Fed through various speaking engagements and interviews tend to give hints to the markets.
Through such venues, the central banks give the markets time to adjust. It is after such repeated instances that the Fed adjusts the Fed funds rate at one of its upcoming meetings.
The markets usually price in the next Fed move
In many cases, the markets are also closely aligned with the Fed. Meaning that the margin of error is very small when it comes to the market expectations.
Combined with the Fed’s communication strategy, the markets pretty much start to discount the news already. The rather magnified movements that one gets to see during Fed days, are usually short-term and short-lived.
How can you take advantage of the Fed funds rate as a trader?
As a trader, it is important to follow the Fed closely. This includes listening to or reading what each of the Fed voting members is saying in the run-up to the next Fed meeting.
Depending on whether you are a long-term or a short-term trader, you can also pick an appropriate trading strategy. For swing traders, the Fed meeting can create a lot of noise. Since such movements are never binary, traders should pay extra attention.
There is a very good chance that a considerable amount of unrealized profits could simply evaporate during such events.
For short-term traders, it is important to be positioned on the right side of the market. Since one view’s the market from a very short-term nature, the markets can be very erratic. Therefore traders should keep this in mind, especially the rising volatility around such periods.
Many forex traders tend to usually rely on technical analysis for trading the Fed meeting. But this alone won’t be enough in the long run. There are moments when the markets can whipsaw as they seek direction. During such periods, it can be easy for traders to lose a lot of money if they do not manage their positions very well.
In conclusion, the Fed funds rate is a very important interest rate that has wider repercussions that go beyond speculative trading. Due to the importance of this interest rate, traders should focus on understanding what the Fed funds rate is all about.
This will help to enhance one’s trading skills as it can invaluable when you start to combine fundamentals with technical analysis or a technical trading strategy.



