A spread in forex trading consists of two elements in the pricing: the bid price, which is the buying price and the ask, also known as the price at which you will sell.
The bid is what a buyer in the market is willing to pay for. This is called going long on a currency pair. The ask is the asking price that a seller is willing to sell the currency pair.
But it is the opposite. When you want to buy, you will accept the asking price and when you want to sell, you will accept the bid from the counterparty.
In other words, as a forex trader, you can sell the currency pair at the bid, and you can buy the currency pair at the asking price. A broker makes money due to this imbalance between the bid and asks prices. Obviously, there would be no opportunity if the bid and ask prices were the same.
It is very rare to find an instrument where the spread is zero. In the forex markets, during periods of high volatility, you can notice spreads falling close to 0 pips, but this is only for a few seconds. By the time you execute this trade, the spread would have widened again.
Learning how spread works can benefit you as a trader. It will tell you whether you need to customize a trading strategy as well as give you insights into adjusting your trailing stops if you use one. Spreads can also help you to avoid picking up obscure instruments as well.
In short, spreads can help you to be more efficient in trading and avoid wasting money.
What does a forex spread do?
A forex spread measures the difference between the bid price and the asking price for an exchange rate or a forex currency pair. You can also call the forex spread the bid/ask spread. This is the price that you pay for buying and selling in the currency markets.
The higher the trading lot size you use, the higher this cost can get. There isn't a broker to avoid paying the spread and there is a broker that will give you zero spreads. The spread cost rises based on the contract size and the tick value.
A forex spread infers the supply and demand dynamics in the financial markets. The bid price shows how much demand there is for the currency pair. When there are a lot of bids, it means that there is a lot of interest to sell.
On the other hand, the asking price shows how much supply is (how many people are willing to sell). If there are more people on the ask, it means that there is a strong demand to buy the currency.
In forex, you are trading the exchange rates. Hence, you will see the prices quoted for a currency pair. This is the price of exchanging one currency for another. For example, a EURUSD rate of 1.1200 means that it takes one euro to buy 1.20 US dollars. The first currency in the forex currency pair is called the base currency and the second currency is called the quote currency.
The rate indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
Example: If it takes 100JPY to buy one US dollar, the expression USDJPY is equal to 100JPY. You can purchase 100 Japanese yen for 1 US dollar.
How can traders calculate the spread in Forex on their own?
The formula for calculating a forex spread is simple: You subtract the bid from the ask.
We know that the spread is a difference between the bid and ask. But depending on the market, the spread can be measured differently. In the stock markets, a spread is measured in cents. If APPL has a bid of $351 and an ask of $351.5, the spread is $0.50.
In forex for example, if the EURUSD bid is 1.2100 and the ask is 1.2105, this means that the spread is 5 pips. A pip is defined as the minimum change in the price of a currency rate. It is the fourth decimal.
Most currency pairs are quoted to the fourth decimal place. One pip represents the last of these four numbers and is therefore equal to 0.0001.
Calculation example: In a EURUSD currency pair, the EUR is the base currency, and the dollar is the quote currency.
If you see a bid price of 1.2104 and ask for 1.2109, then this difference comes to 0.0005.
Because 0.0005 is the fourth decimal, we can now say that the EURUSD spread is 5 pips.
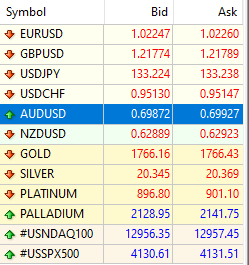
In the above chart, we have the standard MT4 market watch window. Here, you can see the bid and ask prices. The bid price is where you can sell and the asking price is where you can buy at. Thus, for EURUSD, based on the above, the spread is 1.02260 - 1.02247 = 0.00013.
This can be interpreted as the spread is 1.3 pips.
Note that the asking price is always higher than the bid price. In order for your trade to just break even, it must move by the spread amount.
Why is the spread important in Forex?
Forex spread is a valuable concept that you should know. Forex spreads will impact not only your trading costs but also your trading strategies.
A trader who trades with low spreads will have lower operating costs and save in the long run. A trader who trades with high spreads will have to make higher profits to offset the costs. For many traders, the spread is especially important in their losses and profits.
Traders should consider the cost of the spread while trading. But do not get drawn into it too much. If there is a spread of 3 pips, then your price must move a minimum of three pips to break even. Hence, if you are targeting 10 pips, you will make a profit of only 7 pips.
In fact, a spread is a direct initial loss for the trader and the strategy should be to cover the loss during the following trade.
For example, the quote of the EUR/USD currency pair is 1.0905/1.0910. The spread for one lot, in this case, is 5 pips. To cover the loss, you want the subsequent currency pair rate to change by at least 5 pips in your favour.
By calculating the forex spread, you can determine whether the cost is appropriate for your trading style and whether you have suitable trading strategies.
The forex spread is also one of the most important things you should check when deciding on a broker. If you do not know the most basic things about forex trading, such as spreads, you will not succeed. But learning about forex trading basics such as spreads is not that difficult.
As we demonstrated in this article, forex spreads are amazingly easy to understand and read. And all you need to have is some practice.
High spread and low spread
A high spread is when there is a relatively large difference between the bid and ask price. Generally, emerging market currency pairs have a high spread compared to major currency pairs.
Major currency pairs especially those which have a base or quote currency in USD are more popular. Hence, they also enjoy higher volumes and hence higher liquidity. Therefore, spreads for the forex majors are exceptionally low.
On the other hand, if you take exotic currencies like ZAR, NOK, DKK, and TRY, these are not that popular. As a result, the spreads for these exotic currencies are higher than those of the major forex pairs.
Higher than normal spreads are usually indicative of high volatility or low liquidity in the market. A low spread indicates that there is a small difference between the bid and ask price.
Low spreads are usually indicative of low volatility and high liquidity.
If you enter a forex trade when the spread is relatively low, it means that you are entering the trade with a slightly better overall position.
Spreads can widen especially around a major forex news release. Spreads can also widen during economic shocks such as the more recent pandemic or when the Swiss national bank announced that it would remove the EURCHF peg.
The EURUSD has often been used as a comparison for a broker to advertise their spreads. Quite often they talk about the EURUSD spread is as low as 1 pip. While this may be the case, if your interest is in trading other currency pairs, then you should definitely investigate further.
Just because the spread on EURUSD is low, doesn’t mean it will be the same across other currency pairs.
What are the different types of spreads?
There are two types of spreads called the fixed spread and the floating spread.
In a fixed spread, the difference between the bid and ask remains the same no matter what. Even during extreme market conditions, the spreads remain constant. You will see a fixed spread if your broker is a market maker.
A floating spread changes all the time. In a floating spread, there is no guarantee that the spread will remain the same. It will mostly depend on liquidity and demand in the markets. When there is higher liquidity, the spreads will be almost close to zero.
But when there is no liquidity, the floating spread can be wider than the fixed spread.
Traders should understand this key difference when trading the currency markets. For example, it is not logically good to trade exotic currency pairs having a floating spread. By default, the spreads are high and during illiquid market conditions, the spreads can widen.
Widening spreads easily impact your trade’s stop loss and take profit levels. There are both pros and cons to using fixed or floating spreads. Depending on your trading style and activity, you may need to figure this out for yourself.
In many forex forums, you will come across people arguing about the benefits of one over the other. But this is very subjective. As a thumb rule, if you are just a part-time trader, then opting for a fixed spread is good. This gives you a stable spread across the board, no matter what time of the day you trade.
On the other hand, if you are mostly trading during the active trading hours, then a floating spread is better. This is true of the sheer fact that during higher market activity, the spreads can be very small.
Forex spread – Conclusion
To conclude, forex spreads are one of the most basic things you should know about before you trade. If you are a long-term trader, such as swing trading, then it will not be of much consequence. But if you are a day trader, then intraday trading will certainly account for the spreads.
Spreads are unavoidable and can be found in any market that you pick, ranging from forex to commodities to stocks and indices. Depending on the market you want to trade, the spreads can vary. As we outlined earlier, there is no straight answer as to which type of spread is better.
There are both pros and cons with forex spreads (fixed vs. floating). Therefore you need to understand which of these types of forex spreads suits you better. Your trading style and frequency of trades will also play a role.
The more you trade, the more you pay in spreads. Add to this, the additional fees such as swap long and swap short can also eat into your trading charges. Thus, with the spread being one of the easiest, to begin with, start by getting a good understanding of the spreads before you continue your forex journey.
While it may seem a tad complicated at the beginning, if you just monitor the spreads as you trade on a demo account, you will get used to it.
You can also look at forex websites such as myfxbook or forexfactory for example to get a comparison of the spreads charged by different brokers. It can help you to pick the right broker for you.



